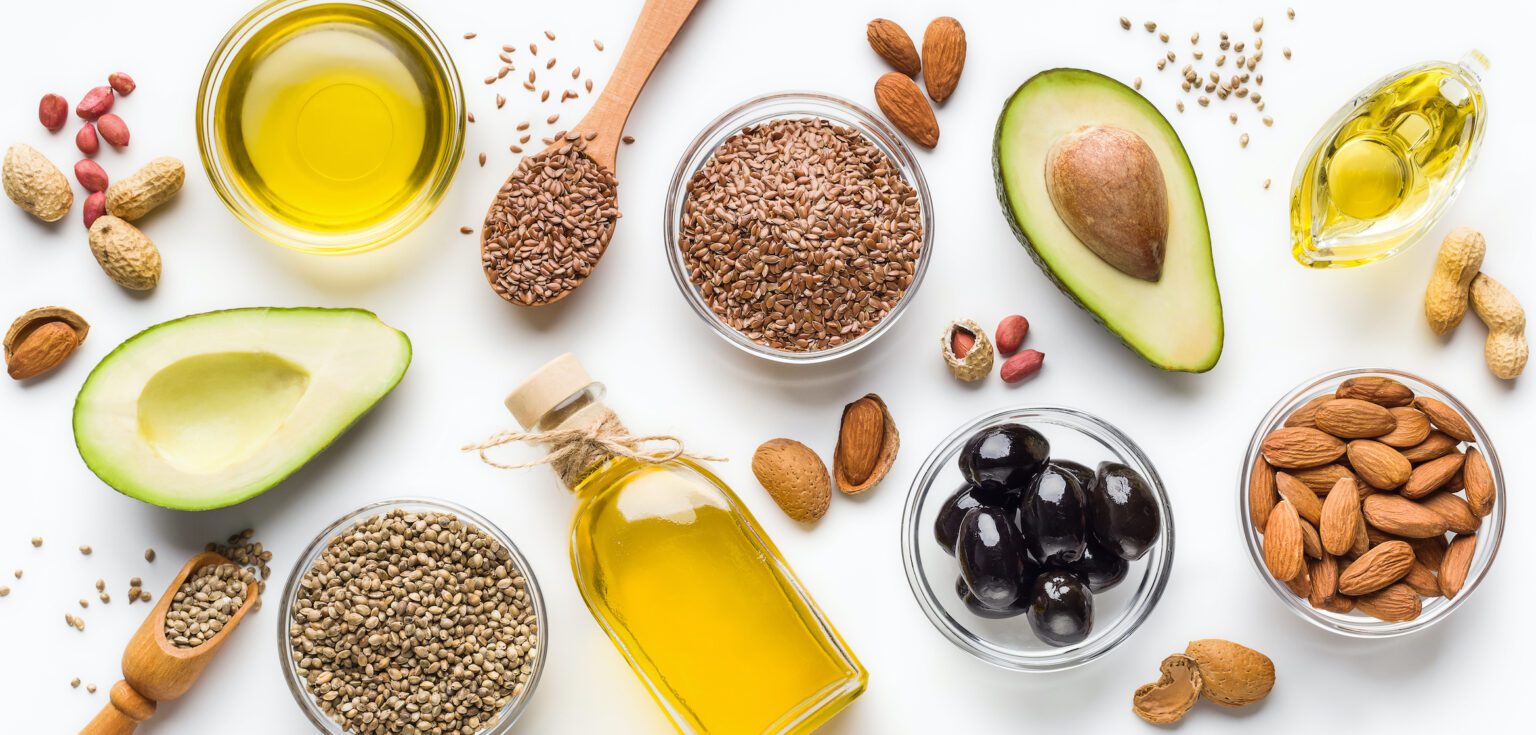
Healthy fats, or dietary fats, are essential nutrients for human life and are critical for our biological functions that keep the human body healthy. Fats can benefit skin, hair, brain health, and the immune system; furthermore, it aids memory, hormone function, and the absorption of certain nutrients.
Recent studies uncover the benefits of a diet regularly, including quality, healthy fat foods. The key to incorporating these healthy fats into your diet is knowing the advantages and that not all fat is the same. We will explain all about healthy fats below.

Benefits of Healthy Fat and the Body
Healthy fats serve numerous critical functions and offer benefits for the human body, with multiple worth noting.
⦿ Energy Provision
Fats are a key and most concentrated energy source in the human body. Fat carries almost double the number of proteins or carbohydrates stored in the body’s tissues and is released when energy is required.
⦿ Structural component
Fatty acids are the most critical component of the lipids within our body, which keep us insulated, aid in cellular communication, and are the main component of our brain composition.
⦿ Carrier or Vitamins
In the diet, fat is a carrier for the fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K, and supports their absorption in the intestines. Consuming sufficient amounts of fatty foods that contain these vitamins is thus essential for adequate intake of these micronutrients.
Other benefits of healthy fats:
- Supports healthy cholesterol levels
- Promotes Healthy Body Composition and weight loss by increasing the feeling of fullness
- Support Healthy Inflammatory Pathways
- Optimizes brain function by increasing cognitive function, memory, and concentration
- Fostering liver and heart health
- Strengthening Bones
- Promoting good sleep
- Improving Skin
- Maintain Healthy Blood Sugar Levels and increase metabolism
An Overview of Healthy Fats
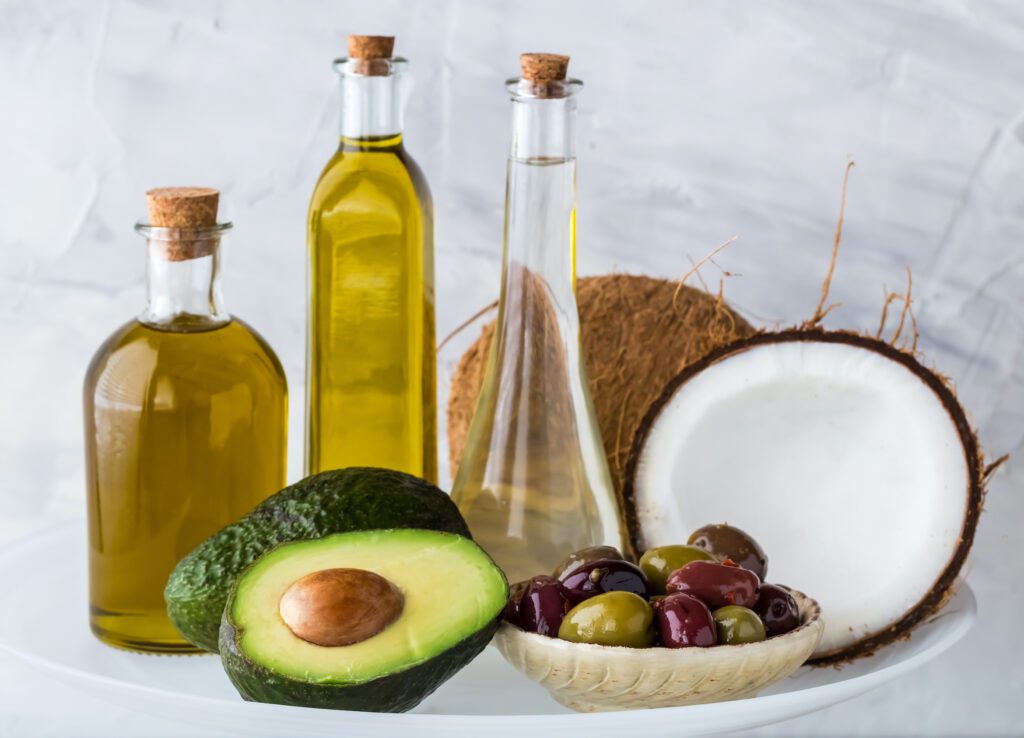


The two types of healthy fats are subdivided into different categories.
1. Saturated fats
These are the most controversial, as not all health experts agree on the benefits of saturated fat. Saturated fat foods should be limited to less than 10% of the daily caloric intake. Noting that healthy saturated fats are naturally occurring and include:
- Hormone-free and grass-fed cheeses
- Grass-fed beef and crate-free pork
- Light, Plant-Based or Grass-Fed Butters
- Non-processed oils such as coconut oil, MCT oil*
*MCT (medium chain triglycerides) oils in recent years have shown to have compounded health benefits that are generally recognized in unsaturated fats, including aiding in heart health, anti-inflammatory properties, digestion, and mood boosting properties.
2. Unsaturated Fats
Recent studies show that eating foods rich in unsaturated fat instead of saturated fat can significantly improve blood cholesterol levels, decreasing the risk of heart attacks and stroke. The two main types of healthy fats are monounsaturated and polyunsaturated.
⦿ Monounsaturated fat-rich foods include:
- Avocados
- Oil-based salad dressings
- Nuts and seeds
- Olives
- Some cooking oils, such as olive, canola, peanut, and safflower oil
Monounsaturated fat is an excellent source of vitamin E, essential for your vision, brain, and skin, and has antioxidant properties.
⦿ Polyunsaturated fat-rich foods include:
- Fish, such as salmon, trout, and tuna
- Oil-based salad dressings
- Nuts, such as pine nuts and walnuts
- Seeds such as flax, pumpkin, sesame, and sunflower seeds
- Some cooking oils, such as corn oil


All of the above foods are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which boost memory and heart health by significantly improving cholesterol levels, reducing blood clotting, reducing irregular heartbeats, and lowering blood pressure.
Dietary Recommendations for Healthy Fats
It’s no secret that a gram of fat is double the calories as its protein and carbohydrate counterparts. But as an integral part of your daily diet, experts recommend that 20-30% of your overall diet comes from fats. The key is understanding the difference between dietary fats and their good and bad health effects.
As our bodies need different types of fats to optimize bodily function. Choose healthy fats, and dodge bad fats such as trans fats, specifically partially hydrogenated oils and saturated fats in processed meats.








